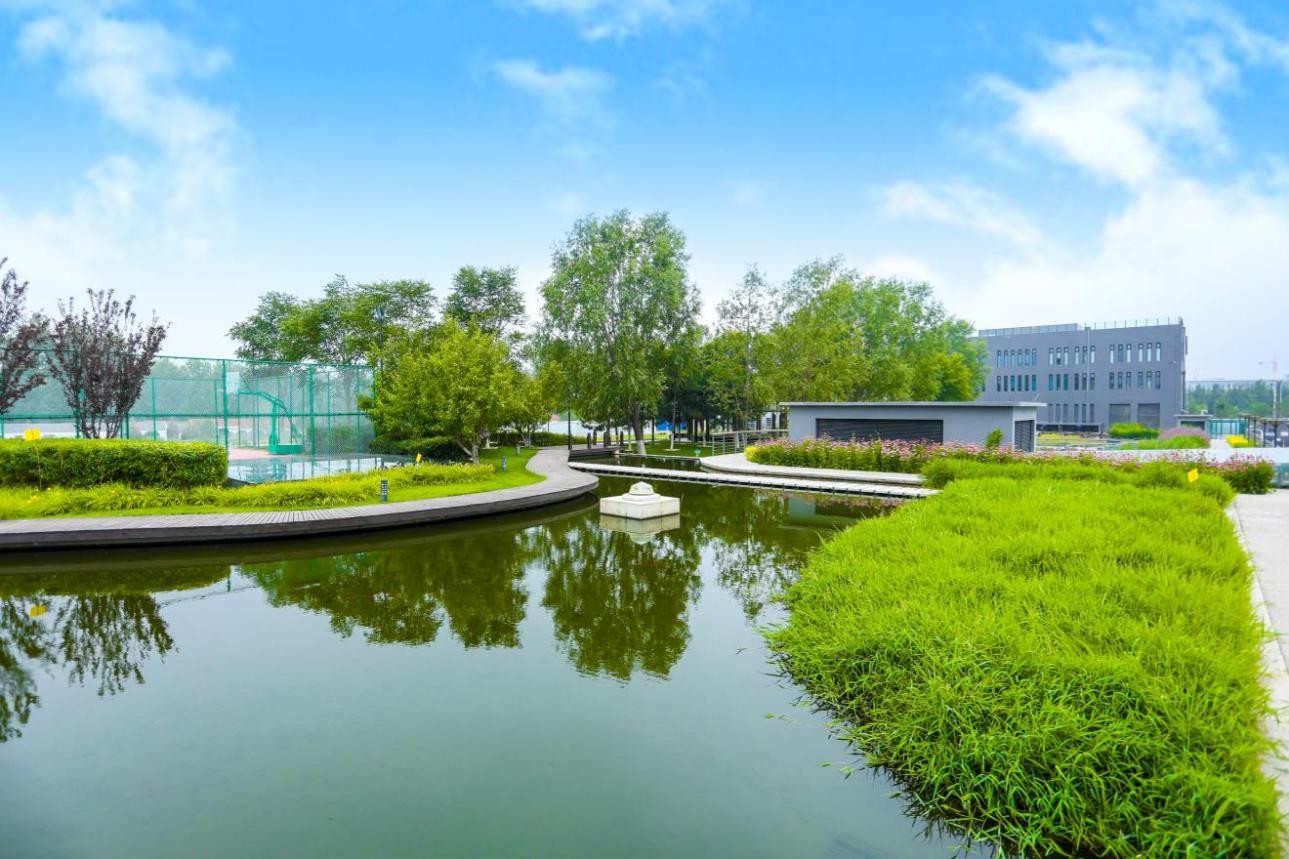
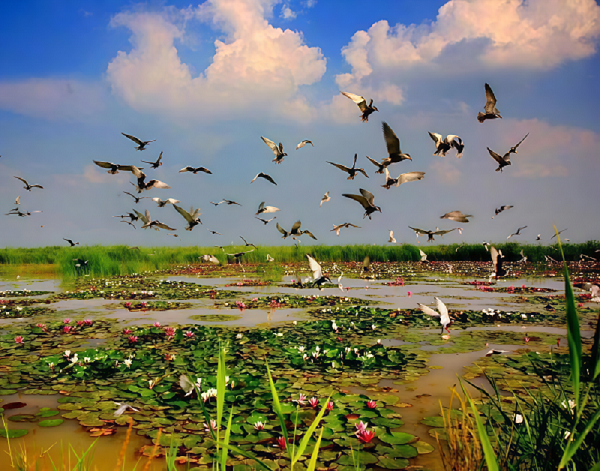
Biodiversity Protection
We actively pursued energy-saving technological upgrades and adopted renewable and low-emission fuels instead of traditional energy sources to reduce the environmental impact of the water purification process. Committed to full-lifecycle ecological protection, we developed biodiversity-friendly products and technologies and actively carried out biodiversity protection and ecological restoration. We actively respond to national initiatives such as the China National Biodiversity Conservation Strategy and Action Plan (2011-2030) and strictly adhere to regulations like the Regulations on the Administration of Construction Project Environmental Protection. Our internal management system, the Biodiversity Protection Management Measures of BEWG1, is in place to continually enhance biodiversity-related governance system. Our overseas operational sites are also in strict compliance with local biodiversity protection requirements, shaping the image of responsible Chinese company.
We adopt the TNFD2-recommended framework of governance, strategy, risk and impact management, as well as metrics and targets, to strengthen the biodiversity governance structure, assess potential risks, clarify action plans, and continuously enhance the Group’s biodiversity management capabilities.
The Board, as the highest decision-making body, is responsible for identifying and determining material ESG matters and proposing recommendations for ESG objectives, policies, and structures. It also oversees the Group's overall strategy and supervises management. The Group established the Sustainability Committee, which oversees the implementation of specific ESG matters, reports ESG management progress and outcomes to the Board, defines material ESG issues, assesses climate-related risks and opportunities, reviews environmental target achievement, and evaluates the Company's ESG impact on stakeholders.
To ensure effective ESG management practices, an ESG Working Group comprising various business and functional departments has been set up to coordinate and drive the implementation of specific ESG projects, regularly reporting to management and the Board to ensure smooth ESG progress and effective risk prevention.
Meanwhile, we have integrated biodiversity protection-related management and oversight functions into the Board of Directors, the Sustainability Committee, and the ESG Working Group to improve the biodiversity governance system.
BEWG has referenced the TNFD-recommended LEAP3 approach to identify, assess, and prioritize the management of nature-related dependencies, impacts, risks, and opportunities material to its operational activities. Building on this, we adhere to a hierarchical action strategy of "Avoid, Reduce, Regenerate, Restore, and Transform"to mitigate biodiversity impacts through a systematic approach across the entire project lifecycle.
Locate
We utilize the Biodiversity Impact Assessment Tool4 and the Integrated Biodiversity Assessment Tool5 to conduct priority assessments of the ecological sensitivity at the Group's key operational sites6. We evaluated operational sites located within 10km and 50km radii of protected areas7 and key biodiversity areas8, respectively. Sites within 10km of protected areas or key biodiversity areas are classified as having high ecological sensitivity. We regularly identify and monitor species listed on the IUCN Red List9 and the China's Red List of Biodiversity10 in these areas, focusing on potential risks and actively deploying preventive and response measures.
Table 1 Biodiversity Impact Assessment Result
| Ecologically Sensitive Zone Assessment Indicators | Amount |
| Number of operational sites with high ecological sensitivity | 29 |
| • Number of operational sites within 10 km of protected areas | 16 |
| • Number of operational sites within 10 km of key biodiversity areas | 20 |
| Number of operational sites within 50 km of protected areas | 38 |
| Number of operational sites within 50 km of key biodiversity areas | 91 |
Table 2 Endangered Species Identification Results
| Ecologically Sensitive Zone Assessment Indicators | Amount |
| Total number of endangered species within 10 km of operational sites with high ecological sensitivity | 59 |
| • Number of species classified as Critically Endangered, Endangered, or Vulnerable on the IUCN Red List | 34 |
| • Number of species classified as Critically Endangered, Endangered, or Vulnerable on the China’s Red List of Biodiversity | 30 |
Evaluate
We utilized the ENCORE11to identify and evaluate the degree of dependency and impact of sewage treatment, water supply, and solid waste treatment business activities on biodiversity. The assessment results were further refined based on the actual operational context of the Group. Based on the materiality assessment outcomes, we will prioritize dependencies and impacts rated as "Very High" to lay the foundation for the Group's biodiversity-related risk management and the development of prioritized biodiversity protection action plans.
Table 3 Materiality Assessment Results of Biodiversity Dependency Factors
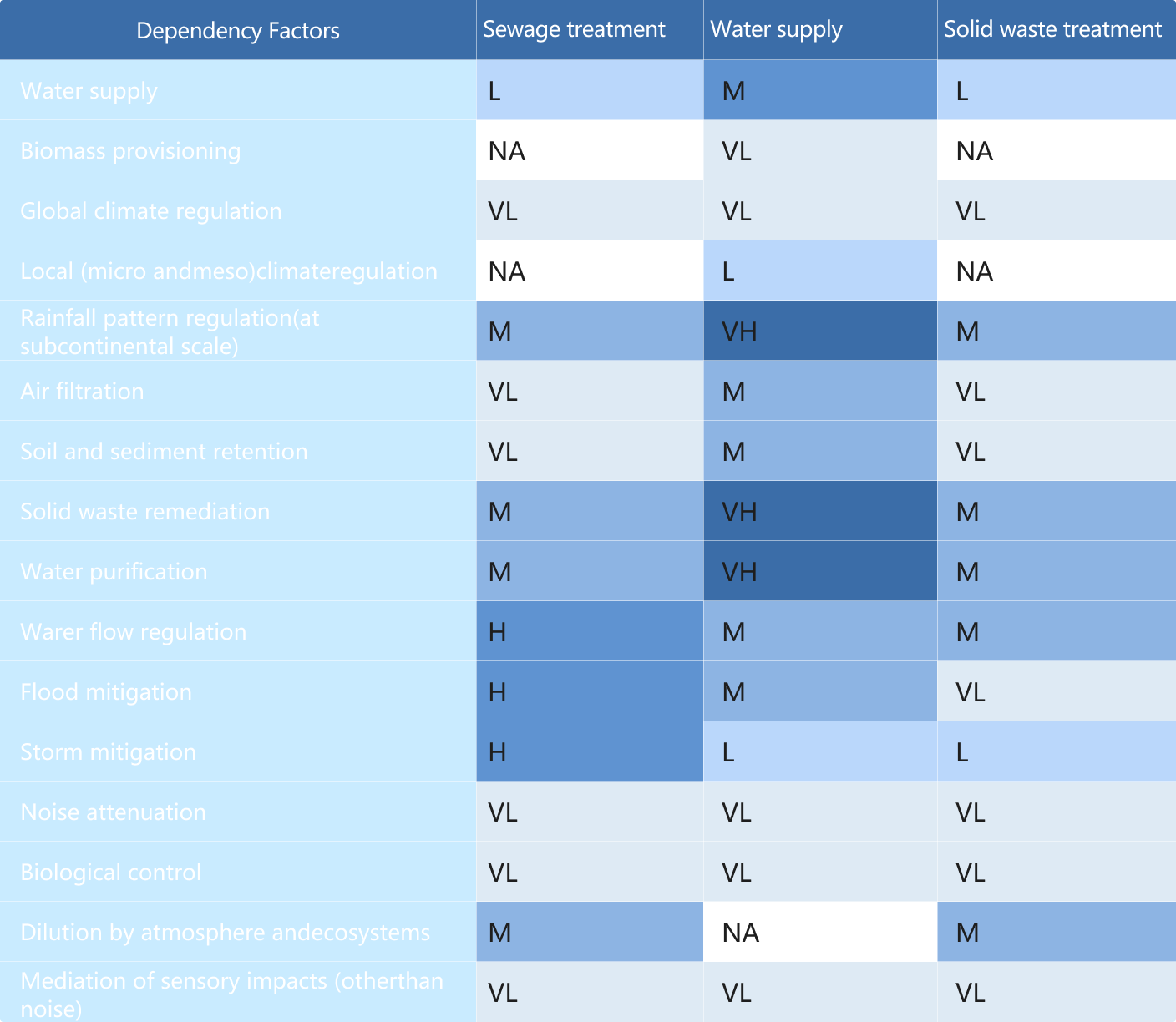
Table 4 Materiality Assessment Results of Biodiversity Impact Factors
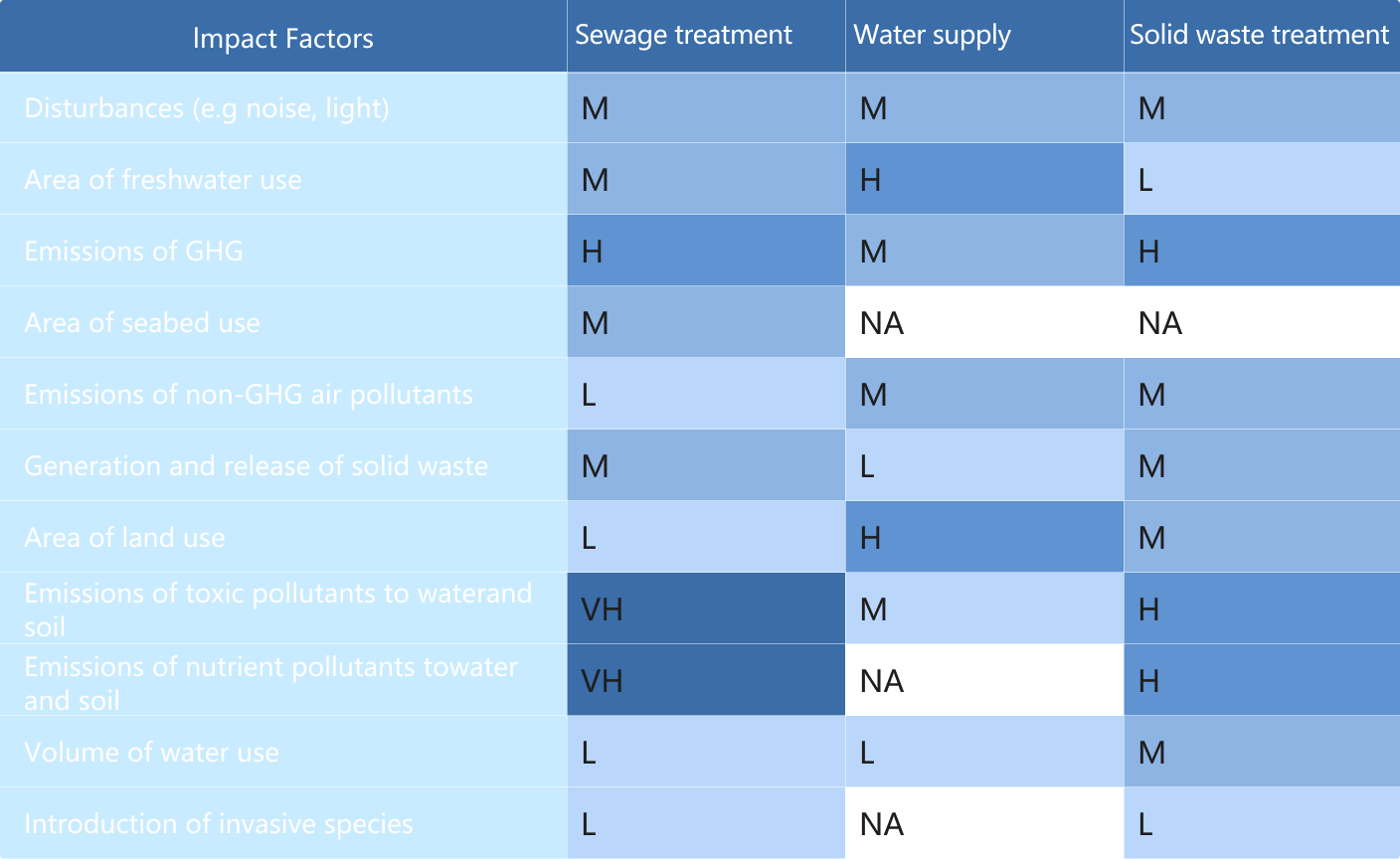
*Legends for Assessment Rating

To effectively achieve the Group's ecological and environmental goals and realize the ecological and social benefits of environmental projects, we have strengthened the analysis of biodiversity-related risks and opportunities, and implemented comprehensive response actions across the categories of "Avoid, Reduce, Regenerate, Restore, and Transform".
Assess
Based on the results of the dependency and impact factor evaluation, we assessed biodiversity risks and opportunities with potential implications for the company, and developed targeted response measures to effectively manage these risks and opportunities.
Table 5 Biodiversity Risk Impacts and Response Measures
| Risks | Risks Impacts | Response Measures | |
| Physical Risks | Rainfall pattern | Regulation of Rainfall Patterns refers to the ecosystem contribution of vegetation and forests in maintaining rainfall patterns at a subcontinental scale through evapotranspiration. Forests and other vegetation recycle moisture back into the atmosphere, thereby generating rainfall. Precipitation in continental inland regions is entirely dependent on this cycle. The reliability of water sources for water supply services depends on the regulation of rainfall patterns by ecosystems to ensure the availability of water sources. Water scarcity may impact the stability of water supply operations, increasing water supply pressure and operational costs. |
Water supply business: • In terms of response measures on droughts, based on the actual geographical conditions of the projects, we increase the frequency of water quality monitoring for water supply projects in drought-prone areas, focusing on potential water quality deterioration issues caused by lowered water levels, and formulate relevant emergency response plans and water volume guarantee measures. • Minimise the impact of water shortages during droughts at the source, by actively encouraging and supporting local governments to prepare backup and emergency water sources. • Reach agreements with water source management entities on prioritising water supply to our projects during droughts. • Connect with the water supply pipeline network of other surrounding water supply entities to achieve mutual supplementation and ensure water supply safety in the event of insufficient water supply within one's own area. • Establish plans for emergency water intake when the water level at water sources is low. • Manage self-use water and reduce the leakage rate in a more effective manner, to better conserve water resources. |
| Solid Waste Remediation | Waste Remediation refers to the ecological contribution of ecosystems in transforming organic or inorganic substances into harmless forms through the actions of microorganisms, algae, plants, and animals. If ecosystems lose their capacity to convert organic/inorganic substances into harmless forms, pollutants cannot be effectively removed by natural processes. This may lead to deterioration of raw water quality, thereby increasing the process costs for water supply business. |
Water supply business: • Attach great importance to handling emergency situations by monitoring water quality anomalies monthly and formulating water quality improvement or emergency response plans for potential risk items, thereby ensuring a stable supply of high-quality water. • The Group has continuously optimised its internal management systems and standards. We established internal control standards and alarm mechanisms for water quality, revised the Standard for Raw Water Quality Grading Warning and the Control Guideline on Water Quality Abnormal Indicator, in which different raw water quality warning levels (I to IV) are designated for indicators such as turbidity, colour, and pH value, based on national standards. Additionally, these Standards provide various water treatment process guidance for water plants under different raw water quality conditions, while improving standardised emergency response procedures and responses to strictly ensure the water quality of the Group's water supply plants. • The Group's water supply projects actively explored and applied advanced treatment processes, and conducted special projects on water quality improvement, aiming to maximise the elimination of raw water quality risks and continuously improve water supply quality |
|
| Water Purification | Water purification services refer to the contribution of ecosystems in restoring and maintaining the chemical condition of surface water and groundwater. Through the decomposition or removal of nutrients and other pollutants by ecosystem components, they mitigate the harmful effects of contaminants on human use or health. Water supply operations rely on the water purification capacity of ecosystems to maintain or improve the quality of raw water, thereby reducing the need for artificial water treatment costs. |
||
| Pollutants release | Improper treatment processes or inadequate sewage treatment methods may lead to the release of toxic pollutants (such as heavy metals and chemicals) and nutrients (e.g., nitrates and phosphates) into soil and water bodies, resulting in pollution. | Sewage treatment business: • We continuously optimise the implementation details of assessments, emphasise the requirements related to influent management and effluent water quality. The effluent water quality of sewage treatment plants is monitored, tested, and evaluated by internal departments, government departments, and third-party testing agencies commissioned by government departments. In 2024, the effluent water quality compliance rate of BEWG’s sewage treatment plants reached 100%. • We established a star-level evaluation system for enterprise operation, to carry out acceptance evaluations with a high-standard operational grading evaluation system and strict management measures, assisting sewage treatment plants in continuously improving their operational performance, stabilizing the effluent water quality performance. In 2024, all BEWG’s sewage treatment plants completed the star-level operational evaluation assessments and acceptance, with 34.4% of the plants rated "three-star" and above, while the high-star plants ratio was gradually increasing. • To promote the deployment of the Group's digital strategy, we continue to deepen the construction of standardised and intelligent sewage treatment plants to improve the quality and efficiency of operation. • In response to sudden influent shock and irregular influent fluctuations faced by sewage treatment plants, we have established an emergency management mechanism for influent shock and a long-term management mechanism for influent shock, consolidated internal and external emergency response capabilities, collaborated with government departments and upstream enterprises, thereby effectively enhancing the operational stability of sewage treatment plants, and ensuring the water quality. |
|
| Transition Risks | Policy | The Ministry of Ecology and Environment issued the China Biodiversity Conservation Strategy and Action Plan (2023-2030), which clarifies the strategic deployment, priority areas, and priority actions for biodiversity conservation in China, providing guidance for advancing biodiversity protection. Failure to promptly respond to policy changes may lead to potential compliance risks. | Sewage treatment, water supply, and solid waste treatment business: • Closely monitor policy trends and changes, conduct regular reviews of laws and regulations, implement employee training and dissemination on relevant legal requirements, and actively participate in discussions within relevant industry associations. • Proactively carry out biodiversity protection efforts at operational sites, integrate protective measures throughout the project lifecycle, and avoid compliance risks. |
| Reputation | Stakeholders such as investors, regulatory agencies, and clients are increasingly attentive to corporate performance in biodiversity. If project operations incur significant negative ecological impacts, it may trigger public opinion crises, potentially leading to diminished client trust, reputational damage to the brand, and other risks. | Sewage treatment, water supply, and solid waste treatment business: • Implement biodiversity protection measures tailored to local conditions to enhance the ecological and environmental value of projects; • Proactively disclose information related to biodiversity protection, and improve the transparency of the Group’s environmental governance through initiatives such as open site visits and online educational videos. These efforts demonstrate the outcomes of biodiversity protection work. |
|
Table 6 Biodiversity Opportunities Impacts and Response Measures
| Opportunities | Opportunities Impacts | Response Measures |
| Policy | As the national and governmental emphasis on biodiversity intensifies, relevant policies are being progressively introduced. The company will play a critical role in ecological protection and restoration projects. | Sewage treatment, water supply, and solid waste treatment business: • Closely monitor national and local policies, regulations, and industry standards related to biodiversity protection, promptly adjust project planning to ensure compliance with policy requirements, and actively seek policy support and funding opportunities. |
| Reputation | By actively protecting biodiversity, enterprises can shape a "green and responsible" brand image, thereby enhancing brand recognition. | Sewage treatment, water supply, and solid waste treatment business: • Expand communication and dissemination channels for biodiversity-related information, and actively showcase progress and achievements in related work. |
Prepare
Based on the assessment results of risks and opportunities, we adopt "Avoid, Reduce, Regenerate, Restore, and Transform" as the guiding principles for biodiversity protection actions. We integrate the concept of biodiversity protection into project operations and develop targeted conservation measures that cover the entire project lifecycle.
Table 7 Direction and Measures for Biodiversity Protection Actions
| Direction of biodiversity protection actions | Protection Measures |
| Avoid | • In the planning and design stage, we conduct ecological basic investigation, assessing the environmental impact, mainly considering factors related to biodiversity protection, with the aim of avoiding the negative impact of the project on the ecological environment from the source; • Focus on preventing and controlling factors like light pollution, noise pollution, and environmental pollution that have impact on the surrounding ecosystem of project sites. |
| Reduce | • We implement regular monitoring, strict abide by environmental supervision systems, establish an environmental management archive, and record in detail environmental monitoring data, abnormal data processing procedures and results; Adopt materials, devices, and equipment that facilitate biodiversity protection; • In the construction stage, we monitor changes in biological indicators during operation in real time with the smart water system, timely identifying biological risks and responding to them promptly; • Implement drainage system renovations to increase sewer network collection rates and reduce unorganized discharge of pollutants into natural water bodies; • Conduct sludge reduction, stabilization, harmless treatment, and resource recovery processes at sewage treatment plants to mitigate risks of soil and water contamination, thereby alleviating pressure on the ecological environment from the source. |
| Regenerate | • Plant vegetation along riparian zones adjacent to water bodies to increase plant coverage and provide habitats for shoreline species; • Establish aquatic biological ecosystems to rapidly restore riverine ecological stability, enhancing biodiversity protection and aesthetic value. • Develop and apply various green infrastructure products and technologies, represented by artificial wetlands. Combining wastewater treatment with ecological protection, we develop green and low-carbon wastewater treatment processes. |
| Restore | • In the planning and design stage, giving priority to the protection of local characteristic species and their habitats, and developing special protection and restoration plans. • Adopt restorative measures, such as creating environments conducive to the survival of species in the food chain to enhance biodiversity on a small scale; • Implement ecological water replenishment projects by diverting high-quality effluent from sewage treatment plants to recharge natural water bodies, ensuring the ecological water demand of aquatic systems is met; • The Group continuously promotes the industry-university-research cooperation, conducts research and development of in-situ water ecological restoration technologies, and furthermore applies them in engineering practices. |
| Transform | • Conduct biodiversity publicity and education for employees, and actively convey the concept, progress and achievements of biodiversity protection to external stakeholders, to advocate green environmental protection and biodiversity protection, raise the awareness of biodiversity protection among all parties, and call on all stakeholders to jointly protect our green homeland. • Conduct specialized biodiversity research and collaborate with national authorities and professional institutions to promote industry-specific and enterprise-specific development; • Establish a star-rated operational enterprise evaluation system to enhance the operational quality and efficiency of water treatment plants. This system comprehensively assesses enterprises across five dimensions: process management, operational quality, business outcomes, personnel capabilities, and digital operational capacity. Indicators such as energy consumption, safe sludge disposal, water quality compliance, and the implementation of eco-friendly public initiatives are incorporated into the star-rating criteria and linked to employee performance evaluations. This approach aims to raise ecological protection awareness among staff and drive water treatment plants to adopt conservation measures. |
"Reduce, Regenerate, Restore, Transform" Actions: Daoxianghu Underground Reclaimed Water Plant
Located adjacent to Cuihu National Urban Wetland Park, Beijing Daoxianghu Water Plant is situated in the northern Haidian District, a critical node of Beijing’s "Western Hills-Yongding River" ecological corridor. As the "Northern Eco-Tech Green Core" of Haidian, it serves as a pivotal zone driving the high-quality development of urban and ecological spaces in the northern region. The plant’s ecological water replenishment and landscape greening projects form an integrated "point-line-plane" ecological network with the nearby Cuihu Wetland Park and Wenquan Park. Simultaneously, the plant’s ecological practices provide environmental support for the construction of Haidian’s Northern Eco-Tech New Area, improving the regional investment and residential environment while indirectly promoting green industry clustering and urban quality enhancement, achieving synergistic unity of "ecological benefits, social benefits, and economic benefits."
The plant adopts a "fully underground treatment + above-ground park" model, with a 20,000-square-meter ecological park built on the surface, featuring a greening coverage rate of over 80%, significantly enhancing regional vegetation coverage compared to traditional plants. The project occupies a total of only 4.66 hectares, saving over 70% of land compared to conventional above-ground plants of similar scale, reducing the occupation of surrounding farmland and green spaces, and providing room for regional ecological reserves, indirectly alleviating the pressure of urban construction on natural ecosystems. Additionally, through technologies such as enclosed underground treatment, multi-stage biological deodorization, and noise control, the plant resolves the issues of "odor nuisance and noise pollution" associated with traditional plants. It features a 200-square-meter water technology exhibition hall and hosts educational activities such as "Ecology Open Days," receiving over 800 visitors annually for exchanges and tours, effectively promoting the concepts of water recycling and ecological protection while serving dual purposes as a recreational space and an educational platform.
The plant utilizes treated high-quality reclaimed water as the core source for ecological replenishment, establishing a complete water cycle chain of "wastewater collection-purification-reuse-ecological restoration" for the Nansha River Basin. In 2024, Daoxianghu Reclaimed Water Plant supplied over 20 million tonnes of replenishment water to the Nansha River. After receiving the plant’s effluent, the water quality of the Nansha River improved from Grade V (inferior) to a stable Grade IV12, resolving the issues of "seasonal flow interruption and black, odorous water." This promoted water flow and exchange in the river channel, enhancing its self-purification capacity. Following replenishment and restoration, the Nansha River has become a "green corridor" connecting various ecological patches, facilitating gene exchange and population dispersal of flora and fauna, and improving the connectivity and integrity of the regional ecosystem.
12 Environmental Quality Standards for Surface Water (GB 3838-2002), Class IV Standards Requirements.
"Reduce, Restore, Regenerate" Actions: Yuhangtang River Water Environment Remediation Project
As a historically significant river in western Hangzhou, the Yuhangtang River suffered severe degradation in water quality and ecological function due to industrialization, urbanization, and human activities. To improve its water environment and restore ecosystem functions, BEWG implemented a comprehensive remediation project for the southern river network, integrating pollution control with ecological restoration to successfully reconstruct a synergistic land-water ecosystem and significantly enhance regional ecological resilience.
The project covers 22 river section with a watershed area of 24.76 km². Through the construction of large-scale storage pipelines, installation of intelligent diversion wells, and physical interception measures in river channels, a systematic solution of "terminal interception + intelligent diversion + large-scale storage" was established. This approach drastically reduced the total pollutant load entering water bodies from the source and addressed overflow pollution caused by combined sewer systems. Simultaneously, systematic aquatic ecological restoration was carried out: emergent plants (e.g., reeds and calamus) and submerged plants (e.g., Vallisneria and Hydrilla) were introduced to reconstruct healthy "underwater forests" and food chains. A "bacteria-algae-mussel" biochain assimilation system was built to purify water quality. Additionally, ecological rehabilitation of riparian zones was implemented using multi-layered, terracing combinations of trees, shrubs, and xeric/hygrophytic herbs, constructing life corridors in land-water ecotones. The complex plant community structure significantly enhanced biodiversity in riparian zones, providing habitats for insects, amphibians, birds, and other species. Current ecological monitoring records indicate:66 species of phytoplankton, 29 species of zooplankton, 5 species of benthic organisms, showing that a stable aquatic food chain has been established. The presence of indicator fish species such as Sarcocheilichthys sinensis and Plagiognathops microlepis confirms fundamental improvement in water quality. The restored area has attracted 51 bird species, demonstrating enhanced terrestrial biodiversity.
"Restore" Action: Xiaotaihou River Water Environment Remediation Project
The Xiaotaihou River, located in the southeastern part of Beijing, serves as a critical aquatic corridor connecting the central urban area and the Beijing Sub-Center. The segment from Kouzi Village to Maying Village was listed as one of the 53 black and odorous river channels in Tongzhou District in 2017. Since July 2015, BEWG has implemented the Xiaotaihou River Landscape Enhancement and Ecological Restoration Project. Today, the aquatic ecological condition of the river has been fundamentally revitalized.
To address the challenges of poor water quality and fragile ecosystems under reclaimed water supplementation in the Xiaotaihou River,BEWG constructed a six-level self-stabilizing ecological structure13 and innovatively implemented mesh-shaped energy flow and material flow regulation technology14. This approach rapidly established a stable, self-sustaining ecosystem, successfully restoring the river’s healthy ecological functions. Current monitoring data indicate that indicator species such as Oryzias sinensis and Rhodeus spp have become dominant populations. Top predators including the Eastern Buzzard (Buteo japonicus), Falcon (Falconidae), and Short-eared Owl (Asio flammeus) have been observed inhabiting the area.
The restored river channel not only functions as a cultural and tourism gateway landscape for the Sub-Center but has also facilitated the natural dispersal of biological communities to the downstream sections of the Xiaotaihou River and the upstream areas of the Liangshui River, radiating and promoting the enhancement of biodiversity across the watershed.
13 It refers to the artificial design and guidance to restore or reconstruct six key trophic levels and functional biological communities within the river ecosystem, thereby forming a structurally complete, functionally sound, and self-sustaining stable ecosystem. These six interdependent and functionally distinct biological community layers include: Submerged macrophyte communities, Emergent and riparian plant communities, Plankton communities, Benthic organism communities, Freshwater fish communities, Riparian animal communities.
14 It refers to an active management technology based on food web and ecological dynamics principles. The core approach involves artificially constructing a "six-level ecological structure" to promote efficient energy flow (transmitted through food chains) and material cycling (such as carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus), thereby rapidly stabilizing the ecosystem and maximizing its purification functions.
"Reduce, Regenerate" Actions: Qingquan River Constructed Wetland Project
The Qingquan River Constructed Wetland Project in Liaocheng, Shandong Province, adopts a combined process of horizontal subsurface flow and surface flow wetlands. It is primarily used for the advanced purification of effluent from Guanxian Wastewater Treatment Plant, with the treated water discharged into the Qingquan River. The wetland is designed to treat 80,000 tonnes of reclaimed water daily, with effluent meeting the Class IV surface water quality standards, and achieving Class III standards for over 80% of the annual operational days. Annual pollutant reduction includes 84 tonnes of COD and 14.6 tonnes of ammonia nitrogen.
The construction and operation of the wetland have not only significantly improved the water quality of the Qingquan River but also created a dynamic wetland ecological landscape for Guanxian County. The wetland has become an indispensable near-natural waterfront recreational space for residents. The wetland covers a constructed area of 150,000 square meters, including 50,000 square meters of open water bodies and 100,000 square meters planted with various aquatic plants, trees, and shrubs. Wetland plants such as cattails (Typha), calamus (Acorus calamus), pickerelweed (Pontederia cordata), water rush (Scirpus validus), yellow iris (Iris pseudacorus), canna (Canna), purple loosestrife (Lythrum salicaria), and lotus (Nelumbo nucifera) bloom in succession, directly expanding the range of biologically available habitats.
Since the wetland’s completion, over 30 bird species have been cumulatively observed and recorded, representing an 80% increase compared to pre-construction records. Winter monitoring recorded a single maximum count of over 100 waterfowl (e.g., geese and ducks). Fish species have recovered from nearly zero to 8 species, and 3 species of amphibians and reptiles have been identified.
"Restore" Action: Daqing Longfeng Wetland Ecological Water Replenishment Project
Daqing Longfeng Wetland, the largest urban wetland in China, plays a critical role in regulating regional climate, mitigating floods and waterlogging, managing stormwater runoff, degrading pollutants, and enhancing the urban environment. Due to its location in a water-scarce city, Longfeng Wetland is facing problems such as the decline of groundwater level and insufficient rainfall replenishment. The effluent quality of the Second Sewage Treatment Plant in Dongcheng District, Daqing City, located in Daqing Longfeng Wetland Nature Reserve, focuses on municipal wastewater treatment utilizing improved A2O (Anaerobic-Anoxic-Oxic) and advanced treatment processes. The effluent quality meets the National Grade 1A Standard, achieving an annual wastewater reduction of 36 million tonnes and providing approximately 102,000 cubic meters of ecological replenishment water daily. This has significantly improved the ecological environment around the wetland, with the bird population increasing year by year.
"Reduce, Transform" Actions: Yixing City Urban Wastewater Treatment Plant
The Wuyi Canal is a key upstream channel in the Taihu Lake Basin, connecting the Beijing-Hangzhou Canal and the Yangtze River to the north, and Gehu Lake and Taihu Lake to the south. It serves multiple functions, including water supply, flood drainage, and navigation. The water quality of the Wuyi Canal directly impacts the quality of water flowing into Taihu Lake. Due to pollutant discharges along its banks, the water quality along the canal has consistently failed to meet the requirements of its functional zoning, making it a critical bottleneck hindering the improvement of water environmental quality in the Taihu Lake Basin.
The receiving water body for the effluent from Yixing City Urban Wastewater Treatment Plant is the Wuyi Canal. Through continuous refinement of operational management and process control, the plant has further optimized its effluent quality while consistently meeting discharge standards. Annual pollutant reductions include over 140 tonnes of total phosphorus and over 1,300 tonnes of total nitrogen, providing significant support for ecological protection in the Taihu Lake Basin. Additionally, the plant actively promotes ecological civilization initiatives by regularly hosting educational tours for schools and community groups, strongly leveraging its role in ecological education. In 2023, Yixing City Urban Wastewater Treatment Plant was designated as a Wuxi City Second-Level Ecological Civilization Education Practice Base.
"Reduce" Action: Qingdao Jimo Sludge Treatment and Disposal Center
Jimo District of Qingdao City is a National Environmental Protection Model City, a China Excellent Tourism City, and a Provincial-Level Civilized City. With the rapid development of Jimo District and the continuous improvement of infrastructure, sludge treatment and disposal issues have become increasingly prominent, including: Growing volumes of sludge requiring disposal; Lack of environmentally friendly landfill facilities;
Inability to achieve harmless reuse; environmental and social problems caused by sludge odor.
Through comprehensive analysis and systematic planning from sludge generation to final disposal, starting with research on the utilization pathways of carbonized residues, BEWG formulated a sludge carbonization process route with a treatment capacity of 300 t/d (at 80% moisture content), adopting the sequence of "deep dehydration + drying + carbonization + flue gas purification +construction material utilization". The carbonization technology independently developed by BEWG features five key characteristics:
• Medium-high temperature pyrolysis carbonization process: No tar is produced during pyrolysis, and the combustion temperature of pyrolysis gas exceeds 850°C, ensuring thorough pollutant decomposition and contributing to stable and reliable system operation.
• Sludge volume reduction exceeding 85%: The final product has a moisture content of ≤1%, with heavy metals solidified in the sludge and nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium retained in the sludge carbon, meeting requirements for land use and construction material utilization, thereby facilitating sludge resource recovery.
• Combustion and recycling of combustible gas generated during carbonization pyrolysis: Reduces energy consumption, sequesters a portion of organic carbon in the carbonized residues, reduces greenhouse gas emissions, and supports the achievement of "Dual Carbon" goals.
• Flue gas emissions compliant with the national Standard for Pollution Control on Municipal Solid Waste Incineration(GB18485-2014) and Shandong Provincial local standards: Emission levels are only 30-40% of those from sludge incineration.
• Oxygen-free pyrolysis process: Eliminates conditions for dioxin formation at the source. Sludge is fully enclosed within the workshop, and sludge odors are co-combusted and purified, effectively avoiding pollution and making it an environmentally friendly sludge treatment and disposal project.
To prevent secondary pollution during transportation, the project adopts in-situ treatment of sludge generated from wastewater treatment plants. Given the highly limited on-site space, we leveraged our proprietary "sludge-water synergy" technical advantage by renovating the original sludge dewatering room of the wastewater plant and modularizing sludge disposal processes distributed across existing structures. This approach achieves efficient sludge treatment and disposal while compactly utilizing land and releasing urban environmental capacity.
"Transform" Action: BEWG (Danyang) Delivers Frontline Environmental Protection Lessons
In recent years, many schools have integrated the concept of ecological environment protection into school-based courses and internship practice courses. Based on this, Beijing Enterprises Water Group (Danyang) Co., Ltd. has become a "learning station" for primary and secondary school students in Danyang and surrounding cities to protect water resources and prevent water pollution. In 2024, schools such as Danyang New District Experimental Primary School, Danyang No.3 Middle School, and the School of Engineering of Zhongbei College of Nanjing Normal University have organized students to come to Beijing Enterprises Water Group (Danyang) Co., Ltd. and visited the water plant's science popularization exhibition hall and sewage treatment facilities to take a vivid and intuitive on-the-frontline environmental protection education course. The event effectively enhanced students' awareness of water resources and water ecological environment protection.
BEWG has established biodiversity protection targets and regularly tracks progress and outcomes in biodiversity protection, thereby guiding and ensuring the effective implementation of all conservation actions.
| Biodiversity Protection Targets |
| • Ensure a balance between habitat protection and sustainable utilization in project development and operational activities, achieving no net loss of biodiversity through measures such as ecological restoration. • Collaborate with value chain partners (including suppliers and contractors) in project development and operational activities to achieve the target of zero net deforestation. |
| Indicators | 2024 | Unit |
| Number of Major Accidents in Violation of Environmental Laws and Regulations | 0 | Case |
| Proportion of New, Reconstruction, and Expansion Projects Conducting Environmental Impact Assessment | 100 | % |
| The effluent water quality compliance rate of BEWG's sewage treatment plants | 100 | % |
| Reduction in COD | 1,117,822 | Tonnes |
| Reduction in ammonia nitrogen | 143,590 | Tonnes |
| Reduction in total phosphorus | 19,711 | Tonnes |
| Reduction in suspended solids | 859,752 | Tonnes |
| Total reduction in pollutants | 2,140,875 | Tonnes |








